Modern organizations rely on easy and secure access to vast amounts of data, which is why they need effective data governance and management. Storing and processing big data is a challenging task, especially when security is an essential requirement. Many on-prem solutions fail with limited scalability, which is why companies are turning to cloud-based data management.
Cloud data management is a process of managing all your stored organizational data with a cloud-based solution. Read the article to learn about the benefits and challenges of this approach and its use cases, and check out case studies for cloud data management.
Introduction to cloud data management
Cloud-based data management consists of the implementation of cloud tools, platforms, and processes to achieve enhanced data storage, processing, and analysis. It may utilize a public cloud, private cloud (on-prem), or a hybrid approach to manage the data. Such solutions are usually owned and managed by public cloud vendors, such as GCP or AWS.
Many cloud data management solutions offer the same capabilities as on-prem solutions, including disaster recovery, archiving, data backup, or analytics. However, the cloud-based approach takes data management one step further, taking advantage of underlying cloud services and addressing special cloud practices regarding security and data integrity.
The growing interest in cloud data management services is due to the expanding complexity of hybrid cloud environments and the amount of data processed daily. Legacy on-prem tools can no longer manage to extract the full value of the data due to their hardware limitations. Cloud-native solutions eliminate silos, simplify operations, and provide a single point of control even for multi-cloud environments.
Cloud data management is a term related closely to cloud computing. Cloud computing is a broader term - it includes delivering cloud storage, processing power, networking, databases, analytics, software, and more via the internet. Cloud data management refers only to the process of storing, protecting, and organizing data in the cloud.
We can help you implement cloud data management as a part of our data engineering services.
Benefits and challenges
The cloud-based approach brings all the benefits of cloud computing to data management. Here is the list of key advantages you can benefit from with this process:
-
Cost efficiency
With cloud data management, there is no large initial investment in physical infrastructure, and the services are billed in a pay-as-you-go model.
-
Scalability
You can easily scale storage and processing capabilities according to your current needs, and resources are available on demand.
-
Accessibility
Resources can be accessed via any device from any location, making collaboration easier.
-
Automatic updates
The cloud services provider takes care of system updates so your environment always has access to the latest features, security measures, and improvements.
-
Security
It’s in the cloud provider’s best interest to invest in security measures and deliver encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications to ensure your data is protected.
-
Backup and data redundancy services
Cloud platforms offer features that reduce data loss, such as disaster recovery and backup copies stored in geographically dispersed data centers.
The benefits of cloud data management platforms sound great, but it’s important to remember there are no perfect tools. Some aspects that raise concern include:
-
Data security
Despite advanced security measures, some organizations consider storing data in the cloud a risk or not compliant with their security policy.
-
Dependency on Internet connection
Accessing data via the Internet is a major benefit, but once the connection is gone, it becomes a remarkable challenge. Connectivity issues can affect access to data and services, disrupting business operations.
-
Vendor lock-in
Relying heavily on specific cloud providers may result in vendor lock-in, making it difficult to change your cloud data management vendor because of price changes or service limitations.
-
Data governance
Maintaining control and governance over data can be challenging in a cloud environment. Organizations need to establish clear policies and controls for effective data management.
-
Complex integration
Integrating existing on-premises systems with cloud-based solutions can be complex, causing temporary issues with data flow between environments.
Cloud data management challenges can be overcome with sufficient planning and by choosing the right vendor. It's important to keep them in mind when switching to this type of solution.
Data Catalog
In today's data-driven world, organizations are accumulating vast amounts of information, making it crucial to establish a comprehensive data catalog to manage and govern this valuable asset. A data catalog serves as a centralized repository of key generic information about data assets, including their location, usage, lineage, and metadata.
This centralized knowledge base empowers data analysts, engineers, and decision makers to easily locate, understand, and utilize relevant data. Assigning data and system severity levels (critical, highly available, standard) ensures that critical pieces of information receive appropriate attention and resources for maintenance. Such classification often works as the bedrock for creating backup, retention, and audit policies in which each class is connected with separate sets of administrative actions and precautions.
By clearly identifying personally identifiable information (PII) data, health-related data, etc. including the purpose for collecting it and the relevant regulations, organizations can maintain compliance with legislation like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA as well as properly safeguard their sensitive data. At this stage, it’s worth embedding control mechanisms to ensure new datasets meet organizational policies before they are introduced in production systems.
All in all, a well-designed data catalog fosters data governance, enhances data discovery, and promotes data-driven decision making, making it an indispensable asset for any organization leveraging data for its success. It’s usually a preliminary step for the other actions described below.
Security and privacy in cloud data management
While cloud data management systems providers do their best to ensure data privacy and security, cyber threats are also constantly developing and becoming harder to address. While a cloud vendor will do its best to ensure data security on an infrastructure level, each and every organization needs to implement proper data governance on top of the generic services provided by the cloud. The very first step on that path might be connected with setting up the aforementioned data catalog and sketching out well-defined and fine-grained access groups, ensuring that your employees have access only to those pieces of information that they need to fulfill their daily routines.
With proper preparation and maintenance, cloud data management can improve your security. Unlike on-prem solutions, there is no risk of data loss due to device failure. Also, cloud providers compete to deliver the most advanced data security measures, including encryption, access controls, and multi-factor authentication. If you implement a hybrid infrastructure setup, don’t forget that the very first security measure to consider is the physical security of your devices - without having that covered, all other precautions might not provide the desired outcomes.
However, concerns persist, and organizations must actively manage and monitor their data to address potential vulnerabilities. Balancing the convenience of cloud storage and the need to protect sensitive data requires adherence to data privacy regulations, clear data governance policies, and ongoing security assessments. Proactive measures, such as regular security audits and employee training, play a crucial role in avoiding risks in cloud-based data management systems. Remember that usually, it’s the employees who are the most vulnerable factors in the entire security setup, so make sure they are well prepared for their tasks and aware of potential threats.
Efficient data storage and analysis
Cloud-based data management leverages scalability, accessibility, and advanced features to provide effective cloud storage and analysis. Cloud services enable organizations to adjust their storage capacity dynamically based on evolving data requirements. With on-demand resources and distributed database architectures, cloud-based data management ensures that data analysis tasks can be performed efficiently and at scale.
Specialized data warehousing services and support for big data analytics tools enable organizations to process and analyze vast datasets seamlessly. The integration of cloud data management with analytics tools facilitates a smooth workflow for data scientists and analysts, resulting in more efficient data analytics and data-driven business decisions.
Cloud data management provides a comprehensive ecosystem for effective and streamlined data storage and analysis, empowering organizations to derive valuable insights from their data assets.
Our data engineering services can help you implement this approach in your company.
Cloud storage and data management case studies
Cloud data management is an approach that is already widely applied in many industries. For example, our team worked with Captor Therapeutics to provide increased security and reliable cloud infrastructure. This client is a biopharmaceutical company focused on the development of protein degradation drugs for cancer and autoimmune diseases. The project’s goal was to ensure the high availability of data to Captor Therapeutics specialists in the most convenient and rapid way, which called for a cloud-based solution. Our team designed and implemented an IT infrastructure and migrated the production environment to the cloud. Due to the sensitive nature of medical data, we approached this project with the highest security standards in mind.
Another example of a cloud data management case study is our cooperation with Procyon. In this project, we developed a next-generation cloud-based privileged access management (PAM) solution designed for multi-cloud and API-based infrastructure. Besides passwordless access management, our team also delivered an automated risk analysis for all permissions granted to all resources across the multi-cloud infrastructure. We ensured enhanced data protection by terminating sessions immediately in case of suspicious activity and provided complete visibility into every deployed resource, user access, and policy.
Popular cloud data use cases
Cloud data management has been proven to work successfully for many use cases. Here are some of the instances where this approach can be used:
- Data warehousing - setting up a centralized repository for structured data, enabling efficient querying and analytics.
- Big data analytics - analyzing large volumes of data using cloud-based tools and services for insights and decision-making.
- Business intelligence - visualizing, analyzing, and interpreting business data for strategic planning with cloud-based BI platforms.
- Data integration - integrating data from various sources in the cloud, ensuring a unified and coherent view of organizational data.
- Data archiving - storing historical data in the cloud for compliance, regulatory, or long-term storage purposes.
- Machine learning and AI - training machine learning models and running artificial intelligence algorithms on cloud-based datasets for predictive analytics.
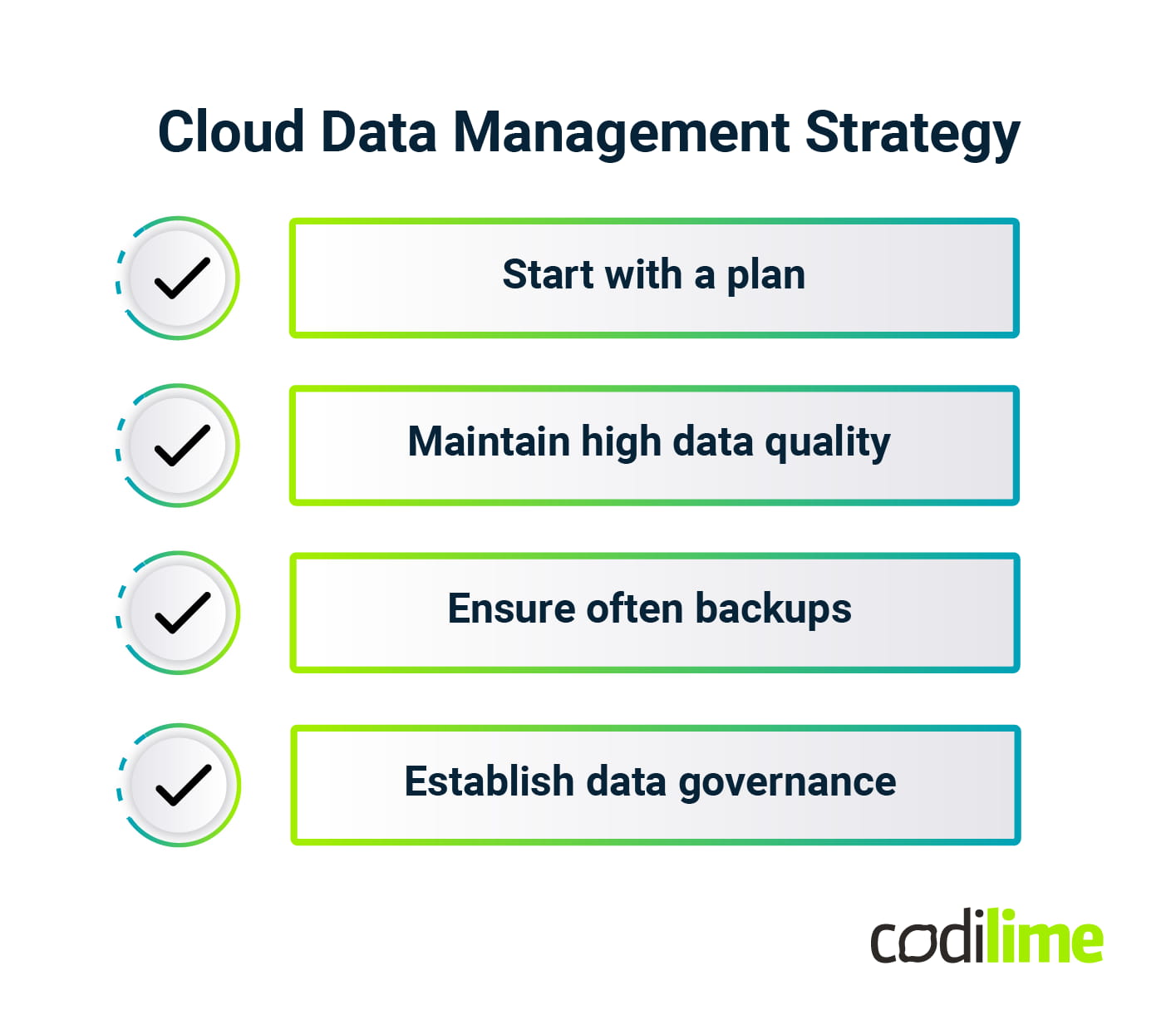
Cloud data management strategy
To implement cloud data management in your organization effectively, you need a proper strategy. Following best practices allows you to fully benefit from cloud services and take your data management to the next level. Here are some principles to keep in mind while creating a cloud data management strategy:
-
Start with a plan
Cloud data management solutions come with their own challenges, and it’s important to be prepared when issues arise. Before implementation, you should assess your organization's requirements and needs, specify what type of data you want to move to the cloud, and, based on that, find the right solution. Some aspects to consider include:
- Do you need a full cloud or a hybrid environment?
- Who will access the data?
- Should you go for ETL or ELT?
- Where should different tasks be processed?
-
Maintain high data quality
Without healthy data, other data management practices are destined to fail. That’s why you need a cloud storage solution that ensures the data is valid and complete. That way, the analytics process can be trusted to provide valuable information for decision-makers.
-
Ensure frequent backups
Usually, cloud data management vendors provide an automatic backup service. However, if the organization uses its own cloud system, it’s important to run regular and frequent backups. In both cases, it’s worth spending time on preparing a clear strategy for data retention, possibly connected with information classification of particular documents or databases.
-
Establish data governance
Cloud data management often brings some data compliance issues. Make sure to update your data policies or create new ones when moving from on-prem to cloud solutions. Also, it might be relevant to update the legal information published on your websites and in applications to cover the means and purposes of storing the data (data processing steps, systems engaged, and transformations, including all necessary metadata), particularly containing PII (personally identifiable information). International laws like GDPR or CCPA enforce tracking user consent for data processing as well as having clear procedures with which your customers can obtain, modify, or delete data about themselves.
The future of cloud data management
Cloud solutions have been a significant trend in technology advancement for a while now, and it’s about time cloud data management gained similar attention. The shift from on-prem solutions to the cloud is not stopping, and there seem to be plenty of cloud advances to come in the future.
One notable trend is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into cloud data management systems, enabling more intelligent and automated decision-making processes. Edge computing is expected to play a significant role, allowing data to be processed closer to the source, reducing latency, and enhancing real-time analytics.
As the volume of data continues to grow, there will be an increased focus on data governance, privacy, and compliance, with the development of more sophisticated tools and frameworks to address these concerns. Furthermore, advancements in hybrid and multi-cloud solutions will provide organizations with greater flexibility in choosing the best cloud services for their specific needs. Overall, the future of cloud data management promises a more intelligent, secure, and agile environment for handling the ever-expanding universe of digital information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud-based data management is becoming more popular every year. It is an effective response to enterprises' current business needs, especially the growing demand for scalable solutions suited to big data. While cloud data management systems come with their own challenges and shortcomings, if they are implemented well, they can completely transform your data operations.








