Do you need to choose a tech stack for your project but don’t know where to start? If so, you’re in the right place.
In this article, you’ll learn what a tech stack is, what tech stack components are, and what the different types of tech stacks are. Further, you’ll find information about choosing the right technology stack for your project and some common tech stacks used by famous companies. Does this content sound interesting? Let’s dive into the world of tech stacks right away.
What is a tech stack?
A tech stack consists of a set of tools and libraries that are combined together to develop an application. Depending on the application you want to develop, the tech stack will differ. Remember that choosing a technology stack determines the application you can build using it, the customization that is possible, and the resources you will need.
Different types of technology stacks
Tech stacks, also known as technology infrastructure or solutions stacks, can be divided into specific fields. One of them is software development, which consists of frontend and backend. Take a look below.
Software development
Frontend
The frontend is the client-side technology. It’s the external part of the technology stack. Basically, it’s what users can see when they use an application. It focuses on the user interface and how the user interacts with the application.
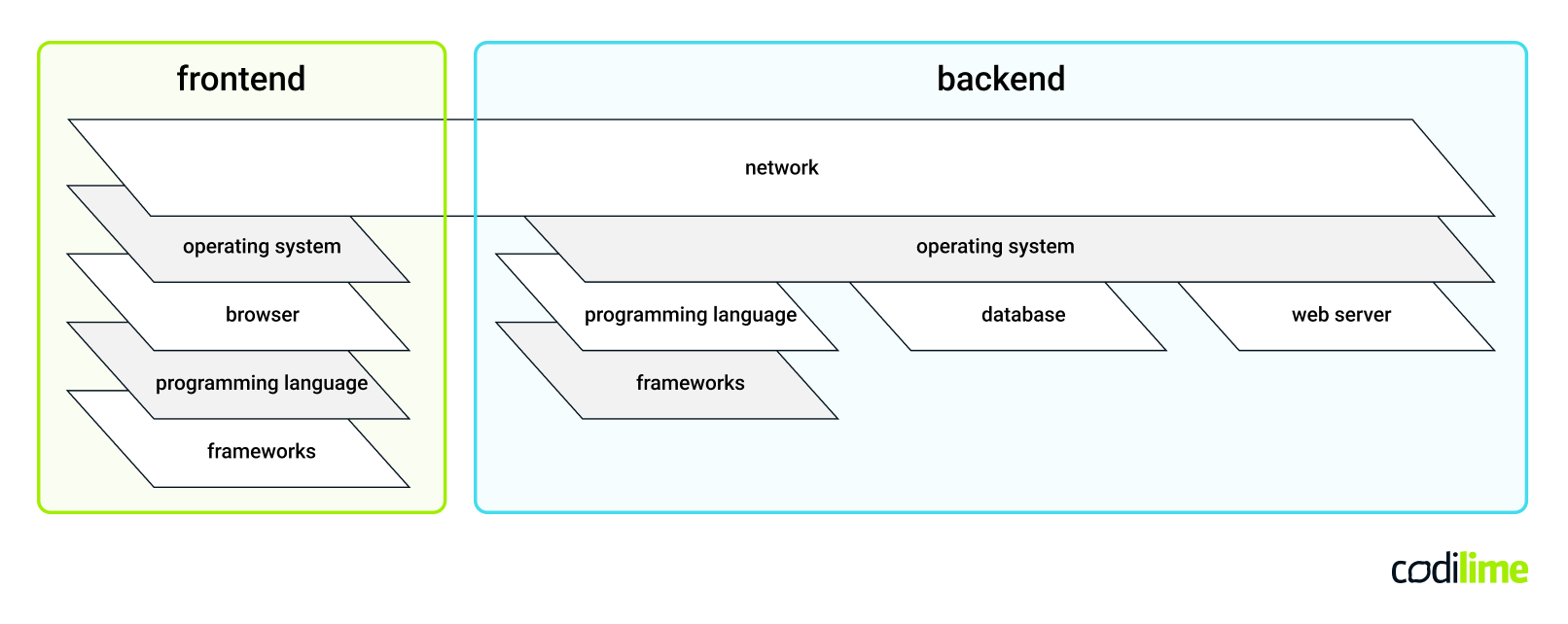
A frontend technology includes:
- HTML (hypertext markup language) - This is often compared to a skeleton. It’s the structure of your application. It puts everything in the right order.
- CSS (cascading style sheets) - If the HTML can be compared to a skeleton, then CSS can be viewed as the skin and the outer appearance in general. It’s responsible for fonts, colors, placing the elements in the right position, layout, and visual elements, etc.
- JavaScript - This programming language gives interactivity to the application. It enables the application to work.
- Frontend framework - Frameworks are used to speed up the development by using provided templates and components. The most popular CSS framework is Bootstrap, and for JavaScript, it’s React, Vue js
, and Angular. You can learn more about frontend frameworks in this article.
Backend
The backend is the server-side technology. The analogy of frontend vs. backend can also be explained using the skeleton example. The frontend is the clothes, skins - the outer appearance - whereas the backend is the skeleton, organs, and muscles. For example, the backend is responsible for authentication and authorization when you log into your account on any website or app. So, thanks to the backend, you can log into your account, and thanks to the frontend, you can see the form and the button and click on it.
Backend technology includes:
- Programming language - There are many programming languages. Some of the most widely used to build applications are, for example, JavaScript
, Python, C/C++, Java, or PHP
.
- Backend framework - A framework facilitates the development process. It enables developers to build applications based on specific components, which are easier to code and maintain. Popular backend frameworks are Django
, Ruby on Rails
, or Next.Js
.
- Database - The database is where the datais stored. Examples: MongoDB
and MySQL
.
- Web server - The server stores, executes, and sends code to users, which is visible as an application. Examples: Apache
, Nginx
, or IIS
- Operating system - The most popular operating systems are Windows Server and Linux.
At CodiLime, we provide backend development services to build a solid base for your project.
Below, you’ll find a graphical representation of what the frontend and backend consist of:
Frontend and backend are common types of tech stack. There are also different technologies that are used for specific and complex software solutions. In this article, we have divided them into the following categories:
Network Solutions
Most network technology stacks can be divided into two groups: open-source networking and vendor solutions. The most popular network services are Linux-based and SDN networks, private and public cloud frameworks, telco, and data center networks.
- Open-source networking - This is an open networking stack from top to bottom. It includes technologies such as P4, Sonic, Open vSwitch, and Tungsten Fabric.
- Vendor solutions - Vendors are providers of technological solutions. Third-party vendors of services are often used in networks. For example, Cisco, Juniper, Arista, F5, or Nokia Networks.
At CodiLime, we have many network specialists who can help you build and design secure network solutions.
Cloud/OS/platforms
Another important type of tech stack is related to cloud expertise. The main activities in this field are building and integrating solutions across public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments. Cloud tech stacks are:
- Public cloud (Google Cloud, AWS, Azure, IBM Cloud)
- Private cloud (Red Hat, OpenStack)
- Operating systems (Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian)
- Cloud-native services (OpenShift, kubernetes, Docker, Envoy)
- Virtualization (KVM, XenProject)
We can support you with the security and integration of cloud solutions. Also, troubleshooting and performance analysis are crucial in building cloud solutions.
DevOps
DevOps is one of the core approaches to software development. Thanks to DevOps, you can build software faster and more efficiently. By combining the development and operations teams, you can improve software delivery speed. DevOps mainly focuses on automation and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) approach. Also, don’t forget about monitoring. It helps gain measurable insights about the product by tracking and measuring the performance. To support the process of DevOps, you can use many tools. For example, GitLab , Puppet
, Vault
, Prometheus
, or CircleCI
.
Data analytics
This tech stack power up data engineering and data science. This allows for processing, storing, and analyzing data. We help turn your data into actionable insights and make better-informed business decisions. Here is an example tech stack:
- Data engineering - Snowflake, Spark, Cassandra, Kafka, Hadoop
- Data science - Jupyter, PyTorch, MXNet, TensorFlow
Let’s also not forget that in today’s world, mobile apps are in very high demand on the market. Most people use at least one mobile application every day. Take a look at the mobile app tech stack:
Mobile application tech stacks
When it comes to mobile applications, technology stacks differ greatly from web app tech stacks. A mobile app has to be developed for a specific mobile operating system, such as Android or iOS.
Mobile apps use cross-platform technologies to build mobile applications. For Android, it is Kotlin , and for iOS apps, it is Swift
.
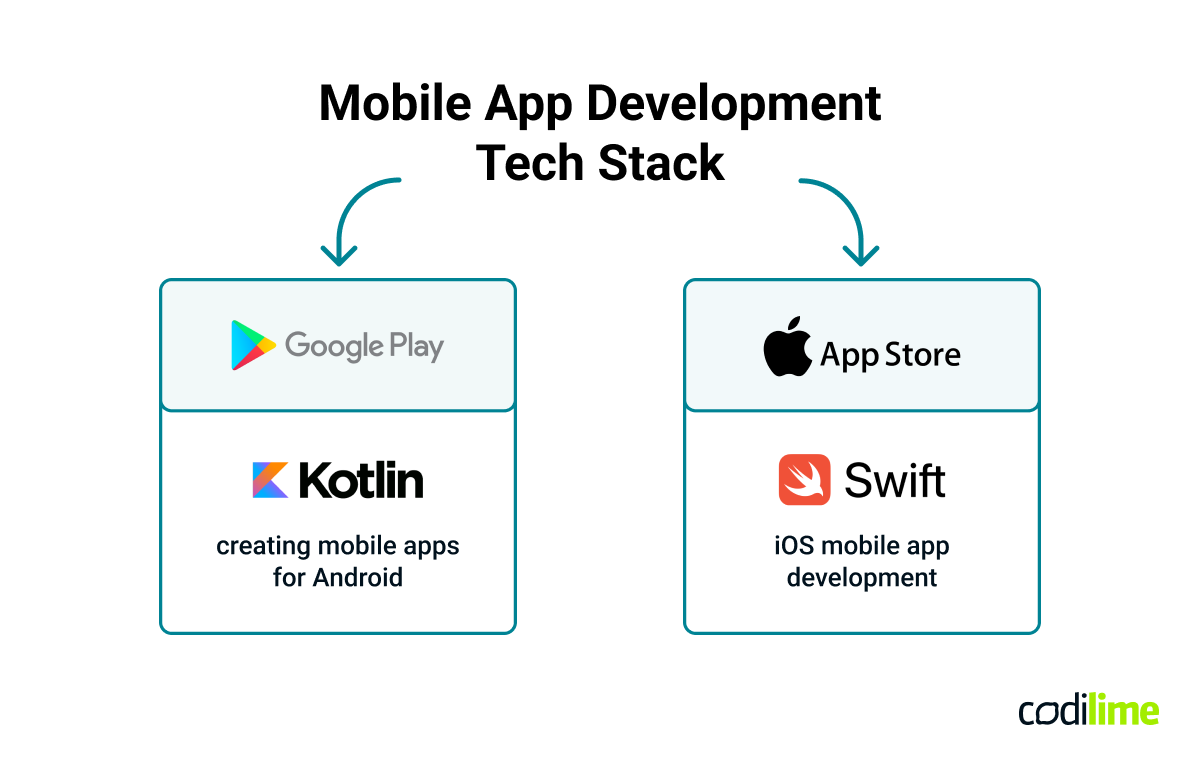
Android and Apple use different technology stacks. So, if you want your mobile app to work on every device, you have to develop two separate versions of it. Conversely, web applications are available for everyone who uses an internet browser regardless of the operating system. Even though web applications run on browsers, they have to be tested on the most popular ones to make sure that they work properly on each of them.
How to choose the right tech stack for your project?
Every application might demand a different tech stack. So there is no perfect tech stack, and it greatly depends on the type of application you want to build. Choosing the right technology stack will help you and your development team to succeed.
Down below, you’ll find a few things to consider before choosing your best tech stack. Some of these we’ve already mentioned in this article, but we want to explain them in depth and highlight the most important issues.
Project requirements
Depending on your client’s needs, you must establish specific project requirements and then decide how big the project will actually be. So, your project size is crucial to choosing a tech stack.
You might use popular tech stacks for smaller projects, but for some more advanced and challenging projects, you might need to build your own tech stack and use more programming languages to reach your goal.
Time to market
How fast do you want to launch your project? It’s good to ask yourself this question before choosing a tech stack. Consider using technologies that offer services and solutions for typical use cases and features. Also, if technology has strong community support, it can help you get new features to market faster. Lastly, choose technologies that are easy to test and understand for your development team.
Scalability
When it comes to tech stack, we can distinguish two types of scalability:
- Vertical scalability - also known as “scaling up”. It enhances infrastructure by adding or replacing additional resources. For example, upgrading the CPU is vertical scaling. Upgraded can also be memory, network speed, or storage.
- Horizontal scalability - also called “scaling out”, which means adding new nodes or machines to handle the increased workload and data processing. However, you have to consider this scaling carefully because it adds complexity to your system. Each machine should have its concrete purpose, and you have to decide how old and new machines will work with each other.
Both of these are essential parts of your project. However, they aren’t easy to achieve. Data storage and queries are difficult to optimize in most cases, but modern databases, such as MongoDB, provide good scaling options.
Whatever tech stack you choose, it should meet the needs of your vertical and horizontal scaling needs.
Security
Apps store a lot of sensitive data, and they need to be secure. For example, security has to be your primary goal if you’re developing software for a medical or financial company. On the other hand, security doesn’t have to be this advanced when building a game app.
Cost
Your budget limitations will influence the tech stack you can use. The market offers many paid and free solutions, so make sure you align them with your needs. If you want to cut costs and speed up ongoing maintenance, the best solution is to use open-source technologies. On the other hand, paid solutions often come with a higher level of customer service and may offer more customization options. Ultimately, the decision of whether to choose a paid or free software solution depends on your specific needs, budget, and preferences.
Examples of popular tech stacks
Popular tech companies might be an inspiration when choosing a tech stack. We’ve prepared a few examples. Take a look at them:
Uber tech stack

Programming languages: C++, Node.JS, Java, Python
Framework: Apache Thrift, Node.js
Databases: M3, Twemproxy, Redis, Hadoop, Cassandra, Riak, PostgreSQL
Server: NGINX, Apache Mesos
Airbnb tech stack

Programming languages: JavaScript, Ruby
Framework: Ruby on Rails
Databases: Hadoop, Amazon RDS, MySQL
Server: NGINX
Spotify tech stack

Programming languages: C++, Javascript, Python
Framework: Hub
Databases: Cassandra, Hadoop
Server: Apache Storm, NGINX
Netflix tech stack

Programming languages: JavaScript, Swift, Kotlin, Python, Java
Framework: WinJS, NodeJS, React
Databases: DynamoDB
Server: RDS and Amazon EC2
As you can see, each of them uses different technologies. This shows how tech stacks differ depending on the application you want to build. At CodiLime, we help build applications by providing custom software development services. We use many popular technologies similar to those mentioned above.
Conclusion
Choosing a tech stack is a major decision for your project. Remember to consider the most influential factors when making a decision. If you're struggling with choosing the right tech stack, CodiLime's expertise can help you make the best decision. A good starting point might be MVP development.








