Implementing UX processes creates a strategic advantage by enhancing user satisfaction and positioning products competitively in the market. This differentiation fosters a positive brand perception and strengthens customer retention, increasing long-term revenue stability.
Moreover, the efficient and cost-effective nature of proper UX design is highlighted, as it reduces development rework, minimizes support costs, and streamlines user interactions, resulting in operational cost savings.
Our webinar UX in Network & Observability emphasized the pivotal role of UX in ensuring success and innovation. This blog post clarifies key insights from the webinar, emphasizing the multifaceted benefits of UX, from brand enhancement and customer retention to data-driven decision-making and future-proofing.
UX: more than just esthetic appeal
Traditionally, UI has received more attention, associated primarily with consumer applications and websites, perceived mainly in the esthetics and interface design. Meanwhile, UX has often been overlooked. However, as we delve deeper into network technology and observability, it becomes clear that UX encompasses much more. It's about crafting experiences that are not only visually appealing but also functionally efficient and intuitively aligned with the user's needs.
UX takes on a nuanced and critical role in network technology and observability. Here, users often grapple with complex data and intricate systems. The challenge lies in presenting this complexity in a way that is accessible, understandable, and actionable. Effective UX in this field can mean the difference between a user effortlessly navigating through a system to achieve their objectives and feeling overwhelmed by a barrage of indecipherable data. It's about empowering users, whether network engineers, system administrators, or IT professionals, to make informed decisions swiftly and confidently.
Understanding and implementing effective UX is not just a matter of user satisfaction; it's a strategic business imperative. In a market where technology products and services are increasingly commoditized, UX stands out as a key differentiator. Businesses prioritizing and delivering superior UX are more likely to attract and retain customers, foster loyalty, and maintain a competitive edge. This approach is particularly vital in network technology and observability, where a product's clarity, usability, and efficiency can directly affect operational effectiveness and decision-making processes.
As we explore UX in the specific context of network technology and observability, we aim to provide actionable insights and strategies. Whether you are a seasoned UX professional, a network engineer, a product manager, or simply someone interested in the intersection of technology and user experience, this blog post offers valuable perspectives and guides you toward harnessing the power of UX in your work.
The role of UX in competitive markets
UX has emerged as a crucial differentiator in the marketplace. This is especially true in the network technology and observability sectors, where products and services are often complex and highly technical. In these fields, the ability to present sophisticated systems in an accessible and user-friendly manner can set a company apart from its competitors.
A product with superior UX elevates itself beyond being just a tool; it becomes an experience that resonates with its users. This resonance can be the deciding factor in a user's choice between similar products. A well-designed UX can be the tipping point in a market saturated with options that sway customer preference and loyalty.
The strategic value of UX plays a pivotal role in various aspects of organizational growth:
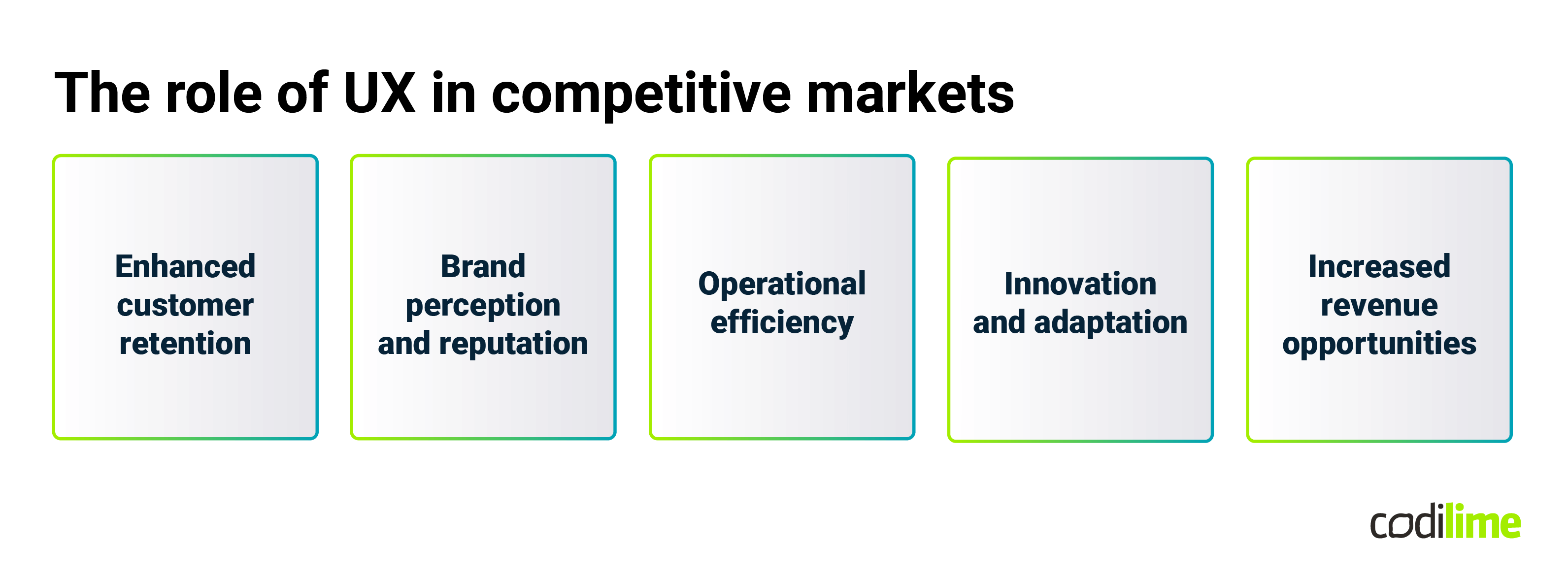
- Enhanced customer retention
A positive user experience fosters a deeper, more emotional connection with the product. This connection can translate into higher customer retention rates. Users are more likely to remain loyal to a product that not only meets their needs but does so in a way that is intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable.
- Brand perception and reputation
UX is a powerful tool for shaping brand perception. A user-friendly product reflects a company's commitment to understanding and prioritizing its customers' needs. This commitment, in turn, enhances the company's reputation, potentially leading to increased market share and industry influence.
- Operational efficiency
Effective UX can significantly streamline operations in network and observability, where the stakes of system management and data interpretation are high. By simplifying complex processes, UX can reduce the time and resources spent on training, troubleshooting, and support. This efficiency benefits the users and translates into cost savings for the organization.
- Innovation and adaptation
A strong UX strategy often involves continuous user feedback and iteration. This approach keeps companies agile and responsive to changing market demands and technological trends. Organizations can innovate and adapt more effectively by staying attuned to users' evolving needs, ensuring long-term relevance and success.
- Increased revenue opportunities
Finally, a compelling UX can open up new revenue opportunities. Satisfied users are more likely to explore additional features or services offered by the company, increasing the potential for upselling and cross-selling.
As we continue to explore the facets of UX in network technology and observability, it becomes clear that its impact is profound and far-reaching, making it an indispensable element in today's competitive landscape.
UX vs. UI - clarifying concepts
User experience and user interface are often used interchangeably. Understanding their distinct roles is crucial for comprehending the broader impact of UX in any organization.
- User Experience (UX): UX refers to the overall experience a user has with a product or service, encompassing all aspects of the end user's interaction. It's about how a product feels, how easy it is for the user to accomplish the desired tasks, and how well the product fits within the context of the user's needs. UX design considers the journey a user takes and the array of interactions they have with a product or service, including aspects like usability, accessibility, performance, design, utility, ergonomics, overall human interaction, and more.
- User Interface (UI): UI is more focused on the product's layout and elements users interact with on their screens. It includes buttons, icons, spacing, typography, color schemes, and responsive design. The UI is a single component of the user's journey; albeit a critical one, as it directly affects a product's usability and esthetic appeal.
Principles of effective UX design
While UI is a significant element of UX, it's only a part of the whole user experience. The broader scope of UX encompasses several elements beyond the mere interface:
- User understanding: UX involves a deep understanding of users, what they need, what they value, and their abilities. It also takes into account the business goals and objectives of the project.
- Holistic design approach: UX design is a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach that incorporates aspects like market research, design thinking, psychology, business strategy, and technology. It's about creating products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users.
- Emotional connection: UX seeks to fulfill the user's emotional needs by ensuring a positive feeling when interacting with a product. This emotional response can be a powerful driver of user behavior and preferences.
- Problem-solving: Good UX design solves real problems. It involves a process of continuous improvement based on user feedback and analytics, ensuring that the product evolves according to user needs.
- Accessibility and inclusivity: UX involves designing products that are accessible and inclusive, catering to the full spectrum of human diversity. This means considering various abilities, languages, cultures, and other factors that influence how users interact with a product.
- Business impact: UX has a direct impact on a business's bottom line. Good UX design can increase customer satisfaction, lower support costs, reduce development time, and increase sales and retention rates.
Understanding the distinction between UX and UI and the broader impact of UX is fundamental for any organization, especially in technical fields where usability and functionality are key. While the UI serves as the interface through which people interact with a product, UX encompasses the entire spectrum of the user's experience. A well-crafted UX goes beyond the surface, creating products that are not only functional and easy to use but also delightful and indispensable to the user.
The business impact of UX specialists
UX specialists play a pivotal role in transforming products from mere tools into solutions that resonate deeply with users. Their expertise is not just about designing visually appealing interfaces; it's about ensuring that every aspect of a product is aligned with the needs, behaviors, and expectations of its users. This alignment is crucial in making products truly customer-centric.
- Empathy and user understanding: UX specialists begin their process with a profound understanding of user needs, often conducting extensive research to gain insights into user behaviors, motivations and pain points. This empathetic approach ensures that product development is driven by real user needs rather than assumptions.
- Design thinking: When employing design thinking, UX specialists approach problems holistically, considering how each element of the product impacts the user experience. They work on creating solutions that are not only technically feasible and economically viable, but also desirable from a user's perspective.
- User advocacy: In many organizations, UX specialists serve as the voice of the user, advocating for user needs throughout the product development life cycle. This advocacy ensures that user-centricity remains a key focus, even when balancing other business considerations.
The influence of UX specialists extends throughout the product development process, shaping how products are conceived, developed and refined.
- Early-stage influence: In the early stages of product development, UX specialists contribute by helping to define the product vision and strategy. Their insights help in identifying key features that will meet user needs and differentiate the product in the market.
- Iterative design and prototyping: UX specialists employ an iterative approach to design, creating prototypes that are tested and refined based on user feedback. This iterative process helps in rapidly identifying and addressing issues, reducing the risk of costly changes later in the development cycle.
- Cross-functional collaboration: UX specialists often work in cross-functional teams, collaborating closely with engineers, product managers, marketers and other stakeholders. This collaboration ensures that UX considerations are integrated into all aspects of product development and decision-making.
- Data-driven decisions: By gathering and analyzing data on user behavior, UX specialists provide valuable insights that inform decision-making. This data-driven approach helps in validating design decisions,prioritizing product features and improvements.
- Long-term product strategy: Beyond the immediate design and development, UX specialists contribute to the long-term strategy of a product. They help in identifying emerging user needs and trends, ensuring that the product continues to evolve and stay relevant in a changing market.
The role of UX specialists is critical in guiding organizations toward a user-centric approach to product development. Their expertise not only enhances the immediate appeal and usability of products but also contributes to long-term business success by ensuring products consistently meet and exceed user expectations.
>> Here, you can learn more about our product design services.
Elements of a great user experience
Here, we explore the core components that constitute an excellent UX, focusing on the importance of intuitive UI, ease of use and performance.
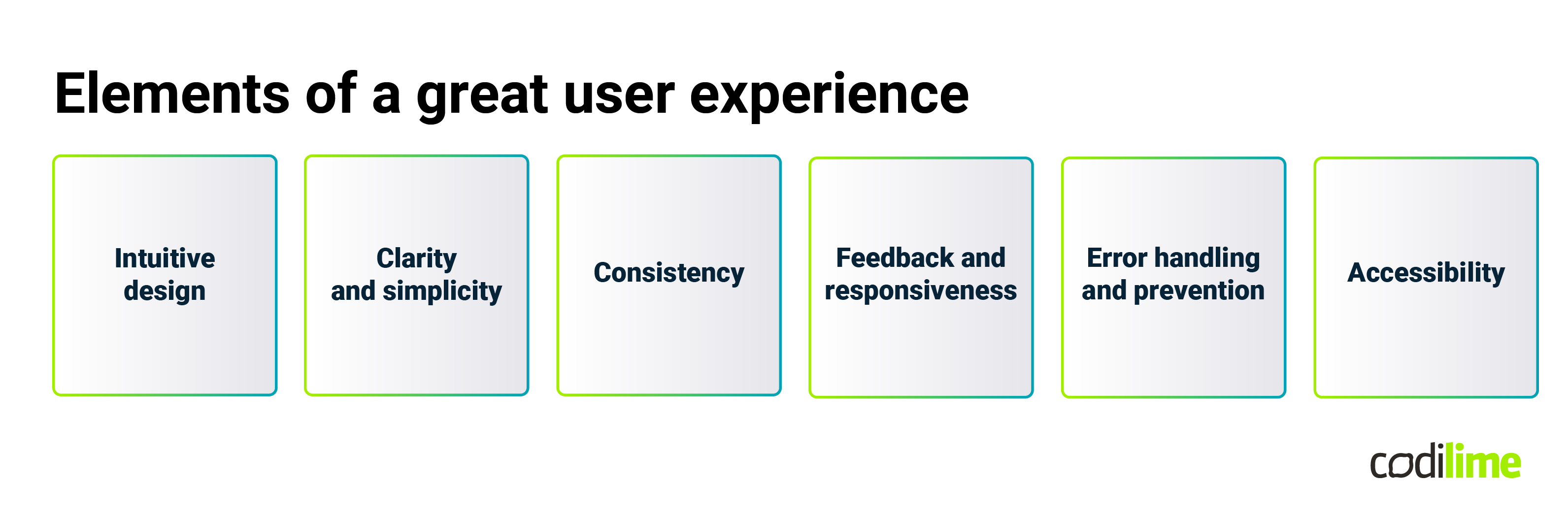
Core components of excellent UX:
- Intuitive design: An intuitive design is user-friendly and easy to navigate. It aligns with users' expectations, enabling them to understand how to use the product without extensive training or reliance on help guides. This intuitive nature is particularly crucial in complex network and observability tools, where users must navigate vast amounts of data and functionalities.
- Clarity and simplicity: Clarity is about making sure that everything in the user interface communicates meaningfully and reduces ambiguity. Simplicity, on the other hand, involves stripping away unnecessary elements and focusing on what's essential. Together, they ensure that the user can easily find what they need and complete tasks efficiently.
- Consistency: Consistent design across all parts of a product enhances the user's ability to predict how it behaves. This consistency can be in visual elements, tone, layout, or even the way certain interactions work. It builds a sense of familiarity and trust, which is essential in professional tools.
- Feedback and responsiveness: A system that responds to user actions and provides feedback makes for an engaging interaction. Whether it's a confirmation message after completing a task or real-time updates, feedback makes users feel in control and informed.
- Error handling and prevention: Good UX design not only handles errors well but also anticipates and prevents them. This involves creating interfaces that minimize the chances of user errors and providing helpful error messages that guide users on how to correct them.
- Accessibility: Accessibility ensures that products are usable by people of all abilities and disabilities. This consideration is critical in creating an inclusive user experience that accommodates a wide range of users.
Besides intuitive UI, ease of use and performance are other significant aspects of UX.
Ease of use is about making complex systems understandable and manageable. It involves designing processes and workflows in a way that they are easy to follow and execute. This aspect is particularly vital in professional environments where time, efficiency and precision are paramount.
Performance is a critical component of UX, especially in high-stakes environments like network monitoring and management. Users expect quick, reliable, and accurate responses from their tools. Performance issues can significantly hinder user experience, leading to frustration and decreased productivity.
UX in the context of observability
In the specialized field of network technology and observability, the role of the user experience (UX) takes on unique dimensions. This section delves into special considerations for UX in network and observability tools and explores the delicate balance between data presentation, clarity, and response time, which are critical for the efficacy of these tools.
- Complex data simplification: Observability tools often deal with vast amounts of complex data. A key UX challenge is to simplify this data without losing its essence. This involves creating interfaces that can present data in an easily digestible format, allowing users to quickly grasp the overall situation and drill down into details as needed.
- Customization and flexibility: Given the diverse needs of users in network environments, UX designs must offer customization and flexibility. This means allowing users to tailor their dashboard views, set up their alerts, and adjust settings to suit their specific monitoring needs.
- Contextual information: Providing contextual information is crucial in observability tools. UX designs should facilitate a clear understanding of the data by incorporating contextual cues. This might include tooltips, help text, or visual indicators that help users interpret metrics and logs effectively.
- Workflow integration: Observability tools are not standalone systems but part of larger operational workflows. UX design should consider how these tools integrate into broader workflows, ensuring seamless transitions between different tasks and systems.
- Scalability: As networks grow and evolve, observability tools need to scale accordingly. UX designs must accommodate increasing complexity and data volumes without compromising the user experience.
How to balance data presentation, clarity and response time?
- Effective data presentation
The way data is presented in observability tools can significantly impact user experience. Designing effective data visualization—such as graphs, charts, and heatmaps—is key. These visual tools should convey information at a glance, helping users quickly understand complex network states and anomalies.
- Achieving clarity
Clarity in UX design involves removing unnecessary clutter and focusing on what is most important for the user. This could mean prioritizing certain types of data, using color coding wisely, or adopting a minimalist design approach to avoid overwhelming users.
- Optimizing response time
In observability, response time is critical. Users expect real-time data and rapid interactions. UX designs must ensure that the tools are not just visually appealing but also performant. This involves optimizing backend processes, ensuring efficient data retrieval, and minimizing latency in the user interface.
- Interactive elements
Interactivity enhances user engagement and comprehension. This could include features like zoomable graphs, clickable elements for detailed data views, and interactive alerts. These features should be designed to provide additional layers of information without adding to the complexity.
Here, you can watch the whole webinar:
Starting with UX: from hypothesis to implementation
This section outlines the process of developing a UX hypothesis and the subsequent steps to initiate and integrate UX processes into projects effectively.
Developing a UX hypothesis based on business objectives:
- Identify business objectives: The first step in developing a UX hypothesis is clearly understanding the business objectives. What are the key goals of the project? Is it to improve user satisfaction, increase efficiency, reduce errors, or enhance decision-making? Understanding these objectives is crucial for aligning the UX strategy with business needs.
- Formulate the UX hypothesis: A UX hypothesis is a statement that outlines how a certain UX change is expected to impact user behavior and, subsequently, business outcomes. For example, a hypothesis could be, "By simplifying the dashboard interface of our observability tool, we will reduce the time it takes for new users to become proficient, thereby increasing overall efficiency."
- Gather user insights: Collecting data on user needs, behaviors, and pain points is essential for validating the UX hypothesis. This can involve user interviews, surveys, usability testing, and analyzing existing usage data.
- Define metrics for success: To evaluate the effectiveness of the UX improvements, define clear, measurable outcomes. These could include metrics like user engagement rates, task completion times, error rates, or user satisfaction scores.
Steps to initiate and integrate UX processes in projects:
- Assemble a cross-functional team: UX integration requires collaboration across different departments. Form a team that includes UX designers, developers, product managers, and other stakeholders to ensure a holistic approach.
- Conduct user research: Deepen your understanding of your users by conducting comprehensive research. Use tools and techniques like user personas, journey mapping, and workflow analysis to gain insights into user needs and behaviors.
- Prototype and test: Develop prototypes of the proposed UX changes and conduct user testing. Gather feedback and iterate on the design. This iterative process helps refine the UX to better meet user needs and achieve business objectives.
- Develop and implement changes: Once the UX design is refined and validated, work with the development team to implement the changes. Ensure that the development process is aligned with the UX vision.
- Measure and iterate: After implementation, measure the impact of the UX changes against the defined success metrics. Use this data to further refine and optimize the UX. UX is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement based on user feedback and changing business needs.
- Communicate and educate: Effective communication about the UX changes and their benefits is key to ensuring buy-in from all stakeholders. Provide training and resources to help users adapt to the new UX.
By following these steps, organizations can successfully integrate UX practices into their projects, leading to enhanced user experiences, improved performance, and, ultimately, the achievement of business goals. Implementing UX is not a one-time task but a continuous journey of learning, adapting, and evolving to meet the dynamic needs of users and the business.
Balancing the investment in UX
Investing in user experience is a strategic decision that can significantly influence the success of products in network technology and observability. This section delves into the cost-benefit analysis of UX investment and highlights real-world examples where effective UX has led to cost savings and efficiency gains.
Understanding the cost-benefit analysis of investing in UX:
Initial investment vs. long-term gains
The initial costs of investing in UX can include hiring skilled UX designers, conducting research, developing prototypes, and user testing. However, these costs should be weighed against the long-term benefits; such as increased user satisfaction, higher retention rates, and enhanced product usability.
Reduced development costs
Investing in UX during the early stages of product development can significantly reduce costs. Well-designed UX can minimize the need for extensive redesigns and reduce the number of iterations required to refine a product. This proactive approach can lead to considerable savings in development time and resources.
Improved user efficiency and satisfaction
A well-thought-out UX design can streamline user workflows, reducing the time users take to complete tasks and improving overall satisfaction. Improving efficiency and satisfaction can lead to higher adoption rates and customer loyalty.
Decreased support costs
Products with intuitive and easy-to-use interfaces often require less support. This can decrease the volume of support calls and queries, reducing the resources needed for customer support teams.
The investment in UX should be viewed not just as a cost but as a strategic investment that can yield significant returns. By enhancing user satisfaction, reducing development and support costs, and improving operational efficiency, a well-designed UX can contribute to both the financial and operational success of products in network technology and observability.
Perspectives on UX: a multidisciplinary view
This section explores insights from various roles, including chief technology officers (CTOs), engineering managers, developers, and project managers, highlighting how different stakeholders perceive and benefit from UX.
Insights from a CTO's perspective:
- Strategic alignment: CTOs may view UX as a strategic component that aligns with the broader business goals. Good UX is vital for maintaining a competitive edge and market relevance.
- Innovation driver: from a CTO's standpoint, UX is a catalyst for innovation. It pushes the boundaries of what is technically possible and what can be achieved regarding user engagement and satisfaction.
- Brand reputation: CTOs understand that the UX of a product is a direct reflection of the company's brand. Superior UX enhances brand perception, fostering trust and reliability in the market.
Engineering managers: balancing technical feasibility with user needs
- Efficient resource allocation: engineering managers appreciate UX's role in streamlining development processes, leading to efficient use of resources and time.
- Collaboration enhancement: good UX practices promote better collaboration between designers, developers, and other stakeholders, ensuring that technical implementations align with user needs.
- Quality assurance: for engineering managers, UX is a quality standard. They see the value in designing technically sound, user-friendly, and reliable systems.
Developers’ perspective: from user stories to code
- Clear requirements: developers benefit from UX as it provides clear and well-defined user stories and requirements. This clarity reduces ambiguity in development tasks.
- User-centric development: UX helps developers adopt a user-centric approach, encouraging them to think beyond code and understand the end user's perspective.
- Problem-solving: Developers view UX as a problem-solving tool. It offers them a framework to think creatively about how users interact with the product and how to enhance that interaction.
Project managers: ensuring smooth UX integration
- Project scope and timelines: project managers rely on UX to define clear project scopes and realistic timelines, considering user research, testing, and design iterations.
- Risk mitigation: effective UX practices help project managers identify and mitigate risks early in the project life cycle.
- Stakeholder satisfaction: for project managers, UX is key to satisfying various stakeholders, and balancing user needs, business objectives, and technical constraints to deliver successful projects.
Understanding these diverse perspectives is essential for integrating effective UX strategies into network technology and observability projects, ensuring that all stakeholders work harmoniously toward delivering exceptional user experiences.
Summary of key takeaways
Wrapping up our dive into UX for network technology and observability, let's highlight the main points:
- UX as a strategic asset goes beyond esthetics and interface design, serving as a strategic asset that can significantly impact the success and differentiation of products in competitive markets.
- While intertwined, UX and UI serve distinct roles. UX encompasses the overall experience and interaction with a product, while UI focuses on the specific elements users interact with on their screens.
- UX specialists are vital in making products customer-centric, contributing significantly to the product development process and decision-making.
- Excellent UX is marked by intuitive design, clarity, simplicity, consistency, responsive feedback, error handling and prevention, and accessibility.
- UX in network and observability - In this niche field, UX must simplify complex data, offer customization and flexibility, provide contextual information, integrate into workflows seamlessly, and scale effectively.
- Investment in UX should be viewed as a strategic decision with long-term benefits, including reduced development costs, improved user efficiency and satisfaction, and decreased support costs.
- Multidisciplinary perspectives - Different stakeholders, including CTOs, engineering managers, developers, and project managers, each perceive and benefit from UX in unique ways, highlighting its multidisciplinary impact.
The importance of UX in shaping the interaction between users and technology cannot be overstated. Whether in the specialized domain of network technology and observability or the broader tech industry, UX remains a critical component for creating products that are not only functional but also enjoyable, intuitive, and empowering. The journey of UX is one of continuous discovery, adaptation, and growth, mirroring the ever-changing landscape of technology.








