IT infrastructure is a collection of components required to manage and operate an organization's IT environments. It can be implemented as part of a cloud computing system or in the company's own facilities. An IT infrastructure is used to support the management of a company or public institution.
This article will highlight the types and elements of IT infrastructure with a focus on IT infrastructure monitoring.
Types of IT infrastructure
When it comes to IT infrastructure, there are three primary types to consider: traditional infrastructure, cloud infrastructure, and hyperconverged infrastructure.
Traditional infrastructure involves companies owning and managing their own data centers, warehouses, and equipment. While it provides full control, it can also be more expensive due to the physical space and power required to house and maintain the components.
Cloud infrastructure, on the other hand, revolves around the components and resources needed for cloud computing. It includes hardware, abstract resources, storage, and network resources. Cloud infrastructure offers advantages such as quick software updates, accessibility from multiple locations, and remote support. However, some organizations may have security concerns compared to traditional infrastructure.
Finally, there's hyperconverged infrastructure, which enables the management of computing resources, network resources, and data storage through a single interface. This integrated approach simplifies operations and enhances efficiency.
Ultimately, the choice of IT infrastructure type depends on the specific needs and priorities of a company. It's important to carefully evaluate the pros and cons of each option to determine the most suitable solution for your organization's requirements.
Regardless of the type of infrastructure chosen, every company should strive to optimize it. Only in this way is it possible to ensure the safety of the infrastructure, minimize or completely eliminate downtime, leverage virtualization to increase availability and efficiency, and better prepare for rapid troubleshooting.
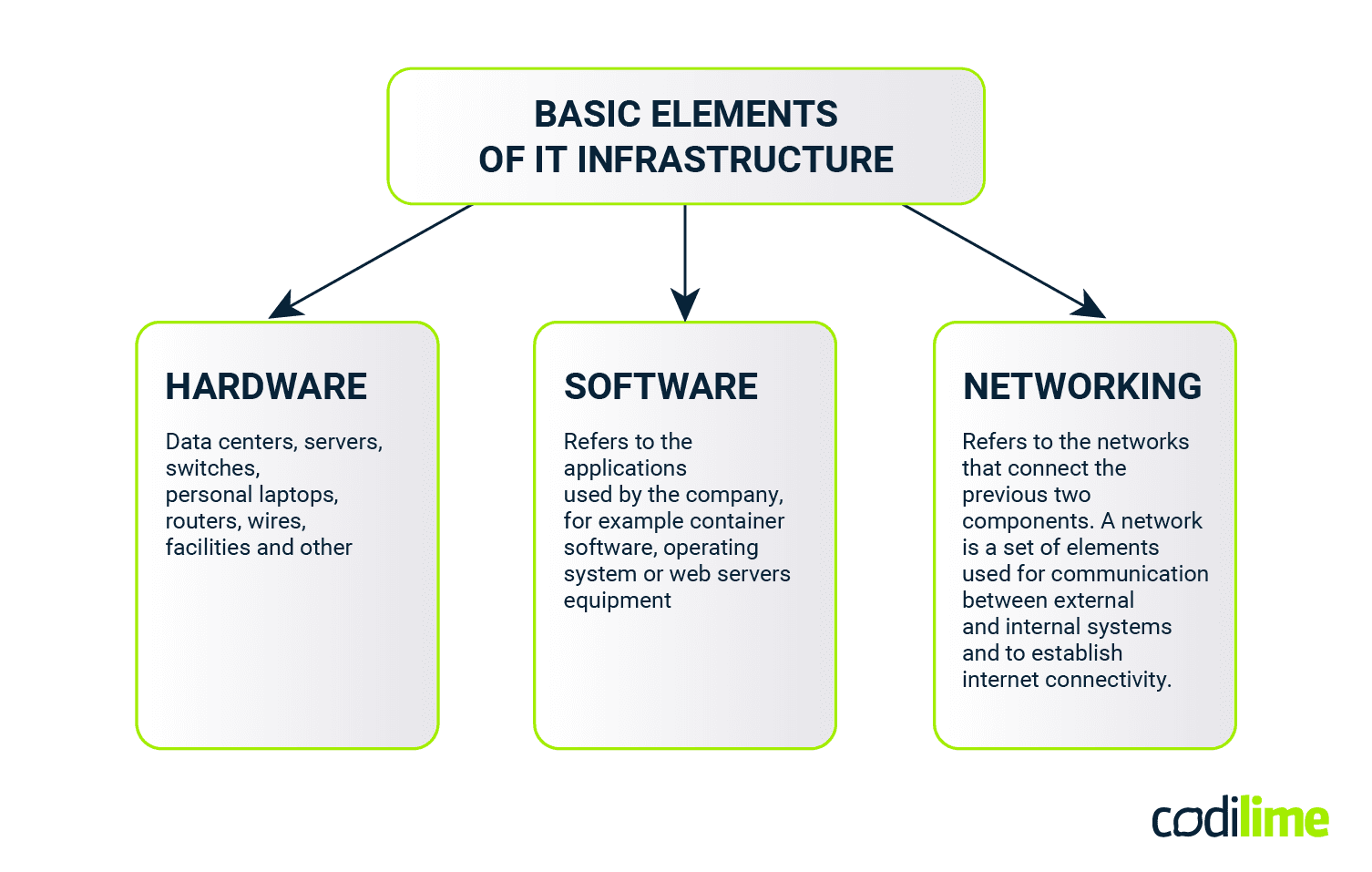
Elements of IT infrastructure
The elements of IT infrastructure typically include of three basic components:
- Hardware: This includes data centers, servers, switches, personal laptops, routers, wires, and various other equipment required for the proper functioning of an IT system.
- Software: The software component of IT infrastructure refers to the applications, databases, virtualization and programs utilized by the company. Examples include container software like Docker or Kubernetes, operating systems, and web servers, among others.
- Networking: Networking encompasses the networks that connect the hardware and software components. A network is a collection of elements used for communication between internal and external systems, as well as to establish internet connectivity.
Depending on the company needs, hardware may be situated in different places (which affects the method of communication with the specific hardware):
- physically in the organization – this choice leads to more resources needed to maintain hardware on the company side. This especially includes fixing problems with hardware, configuration and customization of software on each machine.
- in the cloud – this ensures fast access to memory, computing resources and well defined built-in services without the need to maintain hardware.
Additionally, cloud services offer great benefits like shorter time spent on configuration and installation software, and access to hardware configuration from anywhere (not restricted to the physical location).
On the other hand, cloud has some limitations as well; e.g. it is harder to maintain a high level of security for public clouds as data is stored by an external company (this is why companies should consider their needs carefully). Most cloud services are divided into five categories: SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, XaaS, FaaS.
By considering and managing these fundamental elements effectively, organizations can establish a solid IT infrastructure that supports their technological needs and facilitates seamless operations.
What is IT infrastructure monitoring?
Infrastructure monitoring is essential for the successful operation of any platform or service. It consists of continuous observation of the network, cloud, hardware, application and all elements functioning in this structure. The goal of monitoring is to make the network and IT infrastructure more effective and provide added value for the business. The IT environment has an impact on the entire work of a company. Each malfunctioning element of the network or IT infrastructure can lead to potential losses, unnecessary costs and hinder further development.
Network, cloud and application monitoring tasks include:
- Collecting various data from network devices, such as device metrics, networks, or device configurations.
- Presenting the collected data in a user-friendly manner so that the user can gain useful insights by grouping, filtering or correlating data.
- Create alarms and notifications that transmit information to interested parties like network operators, developers, and managers in a sufficiently short time, allowing an immediate response, thus avoiding unnecessary costs.
- Automatic detection of anomalies in the case of using modern solutions that, with machine learning and artificial intelligence, can analyze data, comparing indicators and events.
What improvements does IT monitoring bring?
- Delivers current information related to the business and the state of the entire IT environment.
- Supports preventive actions and helps prevent failures related to the network and the entire infrastructure.
- Allows creation of detailed analytical visualizations and configured reports.
- Helps to begin repairs quickly in the event of a breakdown.
- Supports increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of network operation.
- Facilitates budget planning for IT maintenance and modernization by monitoring the load on databases and storage.
- Helps to maintain the efficiency of the network, and thus maintain business continuity, increasing user satisfaction.
- Increases the security of data and resources in the organization by monitoring non-standard user behavior and controlling network traffic.
- Helps detect anomalies after configuration changes.
- Facilitates the daily work of IT teams.
- Helps identify performance issues that may be hampering critical business operations.
- Helps in assessing the future needs of the organization. Before an organization updates an app, it can identify persistent usage and storage metrics to decide if more devices and services are required for installation.
What are the key metrics for IT infrastructure monitoring?
Monitoring IT infrastructure is essential for ensuring the reliability, performance, and security of an organization's technology environment. Key metrics for IT infrastructure monitoring can vary depending on the specific goals and technologies in use, but here are some common metrics that organizations often track:
- Availability/Uptime: This metric measures the percentage of time that IT services and systems are available and operational. It's often expressed as a percentage of uptime per month or year (e.g. 99.9% uptime).
- Response time: This metric tracks the time it takes for IT systems to respond to user requests or transactions. It's crucial for ensuring a responsive user experience.
- Resource utilization: Monitoring CPU, memory, disk, and network usage provides insights into resource consumption. High resource utilization can indicate potential performance issues or the need for capacity upgrades.
- Network latency: This metric measures the delay in data transmission over a network. High latency can lead to slow application performance and user dissatisfaction.
- Incident/Event count: Tracking the number of incidents or events, such as system errors, alerts, or security incidents, helps in identifying trends and potential issues before they escalate.
- Error rate: This metric measures the frequency of errors or failures within a system or application. Reducing error rates is critical for system stability.
- Security events: Monitoring the number of security events, such as intrusion attempts or unauthorized access, helps in identifying potential security threats and vulnerabilities.
- Storage capacity: Keeping track of available and used storage space is essential for preventing data loss due to lack of storage capacity.
- Backup success/Failure rate: Monitoring the success and failure rate of data backups ensures data recoverability in case of disasters or data loss.
- Bandwidth utilization: Monitoring network bandwidth usage helps ensure that network resources are efficiently allocated and that there is sufficient capacity to support business needs.
- Patch and update compliance: Tracking the status of software patches and updates across the IT infrastructure is crucial for maintaining security and compliance.
- User activity: Monitoring user logins, activity, and access patterns can help identify suspicious or unauthorized behavior.
- Capacity planning: Forecasting future resource needs based on historical data and trends ensures that the infrastructure can support future business growth.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) Compliance: Tracking whether IT services meet agreed-upon SLAs helps in ensuring that service quality aligns with business requirements.
- Cost Metrics: Monitoring IT infrastructure costs, including hardware, software licenses, and cloud services, helps in optimizing expenses and budgeting.
- Environmental Metrics: Monitoring temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors in data centers helps prevent equipment overheating and hardware failures.
- Power Usage: Tracking power consumption and efficiency can help reduce energy costs and improve sustainability.
- Compliance Metrics: Ensuring that IT infrastructure complies with industry regulations and internal policies is essential for risk management.
- User Satisfaction: Collecting user feedback and satisfaction ratings can provide insights into the overall health of the IT infrastructure from a user perspective.
These key metrics provide a comprehensive view of an organization's IT infrastructure performance, reliability, security, and efficiency. They help IT teams proactively identify issues, optimize resources, and make informed decisions to support the business's objectives.
Log monitoring - an essential component of IT infrastructure monitoring
When writing about IT infrastructure monitoring we can’t omit the topic of log monitoring. It plays a key role for several compelling reasons:
- Visibility and Insight: Log files contain a wealth of information about the health and performance of an IT infrastructure. They record events, errors, warnings, and user activities. Analyzing these logs provides valuable insights into what's happening within the infrastructure.
- Issue Detection and Troubleshooting: Log monitoring helps detect issues and anomalies in real time or historically. When an unexpected event occurs, logs can provide a trail of clues that aid in diagnosing and resolving the problem quickly.
- Security: Logs play a crucial role in security monitoring. They capture activities such as login attempts, access to sensitive files, and potential security breaches. Analyzing logs can help detect and respond to security incidents, including intrusion attempts and data breaches.
- Compliance and Auditing: Many industries and organizations have compliance requirements that mandate log retention and monitoring. By continuously monitoring logs, organizations can demonstrate compliance with regulations and industry standards.
- Performance Optimization: Logs can reveal performance bottlenecks and inefficiencies within the infrastructure. Monitoring logs allows administrators to identify areas that need optimization, such as slow database queries, resource overutilization, or application errors impacting performance.
- Proactive Issue Resolution: Log monitoring enables proactive issue resolution. By identifying and addressing issues before they escalate, organizations can minimize downtime and reduce the impact on users and customers.
- Resource Allocation: Monitoring logs can help in resource allocation decisions. For example, it can reveal trends in resource utilization, helping organizations scale resources up or down as needed to maintain optimal performance.
- Anomaly Detection: Log monitoring tools often include anomaly detection capabilities. These can automatically detect unusual patterns or behaviors within the logs, such as unauthorized access or unexpected spikes in traffic.
- Historical Record: Logs provide a historical record of events. This can be invaluable for forensic analysis, compliance audits, and understanding the sequence of events leading up to an incident.
- Alerting and Notifications: Log monitoring tools can generate alerts and notifications based on predefined criteria. This ensures that IT teams are promptly informed of critical events or issues requiring attention.
- Data Validation: Logs can be used to validate data integrity and consistency. For example, logs can confirm that data transfers and backups have occurred successfully and without corruption.
In summary, log monitoring is a fundamental component of IT infrastructure monitoring because it provides a comprehensive view of system behavior, performance, security, and compliance. It enables organizations to maintain the reliability and security of their infrastructure, respond to issues proactively, and make informed decisions for optimization and growth.
AI, machine learning and IT infrastructure monitoring tools
Using AI and machine learning in IT infrastructure monitoring has revolutionized the way organizations manage and maintain their technology ecosystems. By incorporating these advanced technologies, businesses can proactively detect and address issues, optimize performance, and enhance overall IT operations. Here's how AI and machine learning are playing a crucial role in IT infrastructure monitoring:
- Real-time anomaly detection: AI and machine learning algorithms have the capability to analyze vast amounts of data in real time and identify anomalies or patterns that human operators may miss. They can quickly detect unusual behaviors or deviations from normal operations, enabling IT teams to promptly investigate and address potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach helps minimize downtime and maximize system reliability.
- Predictive analytics: AI-powered IT infrastructure monitoring systems can leverage historical data to make predictive insights about potential problems or performance bottlenecks. Machine learning models can analyze patterns, trends, and historical data to forecast future events and make informed recommendations. By being proactive rather than reactive, organizations can optimize resource allocation, plan for capacity requirements, and prevent potential issues before they impact the system.
- Automation and intelligent remediation: AI and machine learning can automate routine tasks in IT infrastructure monitoring, freeing up IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives. These technologies can automatically categorize and prioritize alerts, correlate events to identify root causes, and even suggest remedial actions. By automating these tasks, organizations can achieve faster incident response times, minimize manual errors, and achieve greater operational efficiency.
- Continuous learning and improvement: Machine learning algorithms can constantly learn and adapt based on new data inputs. As an IT infrastructure grows and evolves, AI-powered monitoring systems can continually improve their accuracy and effectiveness. They can learn from past incidents, fine-tune their anomaly detection capabilities, and adapt to changing environments. This iterative learning process ensures that the monitoring system remains up to date and capable of identifying new and emerging threats or issues.
Top 5 tools for IT infrastructure monitoring
There are many tools available for IT infrastructure monitoring, each with its own features and capabilities. Here are five popular tools for IT infrastructure monitoring
-
Nagios:
- Nagios is a widely used open-source monitoring tool that can monitor servers, network devices, applications, and services.
- It provides a range of plugins and a flexible alerting system for notifying administrators of issues.
- Nagios also offers performance graphing and reporting capabilities.
-
Zabbix:
- Zabbix is an open-source monitoring solution known for its scalability and extensive feature set.
- It can monitor various aspects of IT infrastructure, including servers, network devices, virtual machines, and cloud resources.
- Zabbix supports a wide range of data collection methods and offers customizable alerting and reporting.
-
Grafana Labs stack.
Grafana Labs stack is a set of tools, including:
-
Grafana: Grafana is the core component of the Grafana Labs toolset, and it offers the following features:
- Data Source Integration: Grafana supports various data sources, including Prometheus, InfluxDB, Elasticsearch, MySQL, and more.
- Dashboard Creation: Users can create customizable dashboards with various visualization options.
- Alerting and Notifications: Configuration of alerts and notifications based on data thresholds.
-
Prometheus: Grafana Labs is known for its close integration with Prometheus, a popular open-source monitoring and alerting toolkit. Key features of Prometheus include:
- Metrics Collection: Collect and store time series data.
- Alerting Rules: Define alerting rules for monitoring metrics.
- Scraping: Periodically scrape data from various sources.
- PromQL: Use a powerful query language (PromQL) for data retrieval and aggregation.
-
Loki: Loki is Grafana Labs' log aggregation and monitoring system, which includes features such as:
- Log Collection: Collect, process, and store log data.
- Log Queries: Query logs efficiently using labels and LogQL.
- Distributed and Scalable: Designed for large-scale log processing.
-
Grafana Tempo: An open-source, high-scale, and cost-effective distributed tracing backend for applications. It enables tracing in complex, microservices-based environments.
-
Cortex: Grafana Labs' Cortex is a horizontally scalable, multi-tenant Prometheus-as-a-Service that offers long-term storage, querying, and retention capabilities for Prometheus data.
-
Metrictank: Metrictank is a multi-tenant, highly available, and efficient backend for storing and querying Prometheus metrics at scale.
-
-
Splunk:
- Splunk is a data analytics and monitoring platform that can ingest and analyze data from various sources, including IT infrastructure.
- It's known for its log analysis and visualization capabilities, making it suitable for troubleshooting and security monitoring.
- Splunk offers a wide range of apps and integrations for IT infrastructure monitoring.
These tools vary in terms of complexity, scalability, and cost, so the choice depends on your specific monitoring needs, budget, and existing infrastructure. It's essential to evaluate each tool's features and consider factors like the size of your environment, the types of systems you need to monitor, and your team's familiarity with the tool before making a decision.
Summary
IT infrastructure is an inseparable element of the vast majority of modern enterprises. Depending on the complexity of the domain, the company's resources, and the ability to employ the specialists to serve it, a company's infrastructure can vary significantly. However, it is undeniable that in each case, monitoring of that infrastructure is a necessary procedure. Infrastructure monitoring improves the work of IT teams, allows for early detection of infrastructure problems and gives room for improvement, thanks to the continuous provision of data concerning the condition of the company's infrastructure. Infrastructure monitoring is an activity whose costs (specialists, cloud fees, etc.) are significantly lower than those associated with its absence.



