Python is one of the most popular programming languages. 52% of almost 32,000 voting developers claim that they used this language in the last year. What’s even more interesting, for 29% of respondents, Python was the primary language. Go, despite being less than half the age of Python, doesn’t lag behind - it is in the top 5 programming languages that developers are planning to migrate to or adopt.
In this article, you can find the following information:
- Go and Python features and specifications
- The syntax of these programming languages
- How Go and Python tackle exception handling
- Dependency management in Go language and Python
What is Python? Definition, features and specification
To be specific, in this article we’re focusing on CPython (the original Python implementation). So, please bear in mind that (for the purposes of this article) we’re using CPython implementation as our basis for comparison.
Python is described as:
- high-level - it enables the writing of programs that are independent (more or less) of any particular type of computer. It’s considered closer to human languages and with strong abstraction from the details,
- interpreted - it isn’t directly converted into machine code. Instead, there is an interpreter changing the written code into language understood by the computer's processor,
- procedural - common tasks are placed in functions, and the other tasks are treated as iterations,
- object-oriented - supports programming using a classes and objects paradigm,
- having dynamic semantics - uses variables as dynamic objects. In Python, variables store references
to underlying values or objects. Everything together means you can assign variables in a way that makes more sense to you than to the computer.
Python combines dynamic typing (each variable is determined only during runtime) and dynamic binding - the variable is bound to a type, instead of being specified by a declaration statement. Python has a lot of built-in data structures, and it is a general-purpose language, so it isn’t specialized for any specific problems.
We could take the Python Language Reference as being the closest to the language specification. You can find there the description of the syntax and the often-used semantics.
Is Golang interpreted or procedural like Python? Let’s check.
Definition of Go. What are the features of this programming language?
If we’re talking about Go language features, it is necessary to mention that this language is:
- open source - its original source code is freely available and may be redistributed and modified according to user needs and preferences,
- procedural - procedures (functions) are connected to form a program,
- compiled - the opposite approach to interpreted languages. In this case, code written in a compiled language is directly converted into machine code, which is executable by the processor,
- statically typed - type checking is performed during compile time,
- concurrent - functions can run independently of each other,
- with built-in support for concurrent processing.
Go has both the features of statically typed languages (high performance, type safety) and dynamically typed/interpreted languages (conciseness, expressiveness, better readability).
An example of Go’s shorthand variable declaration type safety and conciseness is presented in the table:
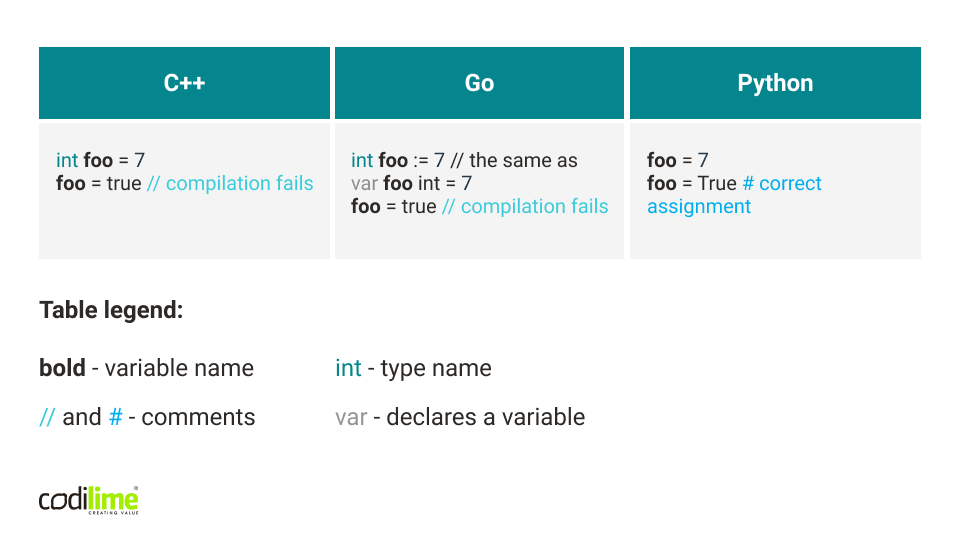
In this scenario, we declare an integer variable and later we try to assign a boolean value to it. As we can see, Go and C++ prevent changing the variable’s type. However, Go’s variable declaration doesn’t require an explicit type statement - it is inferred from the assigned value type.
Here we mentioned C++ only as an example in our table. If you are curious how C + + is different from Go and Python, check out our blog post, where we covered the main aspects.
To dig deeper into the Go programming language specification, you can click here , and get answers for every question which comes to mind.
But how exactly are these programming languages different from each other during day-to-day use?
What are the Go and Python languages used for?
Go and Python both have their advantages and disadvantages. There are no strict guidelines to follow, but each programming language has specific features that perform better in certain fields. Let’s see how Go vs Python uses languages for.
Go could work ideally with on-demand services, cloud services, or media platforms. This programming language also provides a resource for coding network servers - especially web servers and microservices. Go might be the perfect fit for your project.
On the other hand, Python is used in many diverse fields. This programming language provides a vast amount of machine learning and AI libraries and packages. Moreover, as an open source project, Python gives a lot of graphing libraries. It is also used in data analytics, web development and programming applications.
Libraries in Go and Python
Programming languages use libraries, which consist of prewritten code, configuration data, documentation, and help data. These libraries can also include subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. Using libraries facilitates coding process.
Go and Python provide organized information about libraries, frameworks and software on their websites:
Is code coverage important?
This metric helps in monitoring the code's performance and quality by displaying how many lines of code successfully pass the test process.
The Go team upgraded the test coverage tool with the introduction of Go 1.2. They examined the current test coverage tools and removed any flaws, such as complicated implementation. Rob Pike, one of the Go language's developers, explained the entire Go cover story.
Python has a specific tool called coverage.py for assessing code coverage, but be aware that it only works with certain versions. You may also take into account pytest, a framework for creating simple and large functional tests for applications. Another framework devoted to unit testing is Unittest.
Both Go and Python allow you to test the code, although the Go tool appears a little more flexible.
What are the differences between Go language and Python?
Go and Python cannot be simply compared to each other based on their features alone, such as whether they are high-level programming languages, etc. However, there are crucial aspects of both programming languages which we can compare: readability, speed, error management, libraries, concurrency and community. Taken together, these will create a more precise description of Go vs Python.
Readability levels in Go and Python
Readability indicates whether a specific programming language is easy to understand, read and learn. Usually, if the language has a higher readability level that means it will be easier to debug and you'll be able to write an application faster.
What does syntax look like in Python and Go?
The syntax is the foundation if we’re talking about readability. Syntax is all about using specific words in a predefined order to create commands understandable by the computer. Are there any differences in these programming languages’ syntax? Let’s check.
Syntax is one of the aspects that influences readability level. Let’s look at how static and dynamic typing can change the readability for better or worse.
In Python, as a dynamic language, not every function is documented. That sometimes forces you to dig deeper into implementation, or alas, you will have to guess what input parameters are expected. Go, as a statically typed language, hands everything to you in regard to input type. Python syntax is quite dense, but uses a lot of English words. That makes it more understandable and easier. One of the Python principles says: “There should be one — and preferably only one — obvious way to do it.” With this mantra in mind, the newly-created syntax is possibly the easiest and most consistent. Nevertheless, you have to keep track - Python syntax changes with each new version of the language.
One of the Go programming language’s strengths is its minimal syntax - it has stayed almost the same, without any great changes in recent years. Thanks to that you have a guarantee that applications written in the older Go language version will still work. That means developers haven’t had to learn new paradigms or syntax. What’s more, there is only one standard code format.
Everything from the above indicates Go’s strength, until you want to write code that isn’t strictly based on the syntax. The Go programming language doesn’t leave you a choice - you have to be loyal to gofmt. Python gives you a helping hand - PEP 8 . PEP 8 is a guide full of conventions to extend and enrich the standard Python library and is considered a formatting standard for Python projects.
Is Python faster than Go?
To properly compare the speed of these languages, a few tasks were chosen to show how fast Go and Python can resolve them.
- Mandelbrot - Python 3: 163.32 secs vs. Go: 3.73 secs.
- Fannkuch-redux - Python 3: 352.29 secs vs. Go: 8.31 secs.
- K-nucleotide - Python 3: 46.28 secs vs. Go: 7.46 secs.
- n-body - Python 3: 567.56 secs vs. Go: 6.38 secs.
- Reverse-complement - Python 3: 7.20 secs vs. Go: 1.35 secs.
- Binary-trees - Python 3: 48.03 secs vs. Go: 12.23 secs.
- Pidigits - Python 3: 1.28 secs vs. Go: 1.00 secs.
- Regex-deux - Python 3: 1.36 secs vs. Go: 3.85 secs.
As you can see, only in one case was Python faster than Go. What, as in the n-body case, makes Go 89 times faster than Python? This isn’t an isolated example - in Fannkuch-redux, Go is almost 43 times faster. The main reason why the difference is so glaring is the fact that Go is a compiled language in contrast to the interpreted Python. The Go programming language also has one more advantage: Goroutines. These lightweight threads need less RAM and are managed by Go runtime. In comparison to traditional threads (as in Python) Goroutines utilize less resources. What’s more, multithreading in Python couldn’t be taken literally - Python programs are single-threaded with the possibility to add concurrent routines.
But speed isn’t the only important aspect when creating an application. Exception handling can be a critical factor when choosing the programming language that is best-suited to your needs.
Error handling in Go and Python - a comparison
To be specific, we’re thinking about exceptions. An exception is anything anomalous which demands special/different processing. They are not caused by errors in syntax. Handling exceptions guarantees that the program flow isn’t interrupted when an error occurs.
How do the Python and Go programming languages deal with exceptions?
Exception handling in Python
In Python, you can handle exceptions with three statements:
- try
- except
- finally
Statements between try and except all together create a try clause.
There are a few possible scenarios when you execute a try clause:
- There is no exception - after executing the try statement, the except statement is passed over, and the try statement is finished.
- There is an exception - if the exception matches the one named in the except statement - this clause is executed, the rest of the try statement is skipped.
- There is an exception, but it doesn’t match the exception mentioned in the except statement - this is an unhandled exception, and execution is stopped.
The finally statement is executed in any event. This is only a cursory explanation of how exceptions are handled in Python - on their official site , you can find a more complex tutorial.
Digging into this topic deeper, you can also come across a raise statement. This statement helps in raising the exception - it is simply being forced to occur.
But you have to be aware that you should use this statement only in emergency situations. This isn’t a solution to control program flow.
What does the exception handling process look like in Go? Keep reading to find out.
Exception handling in the Go programming language
Go, similarly to Python, provides three statements:
- defer
- panic - don’t use this statement as regular error handling. The better choice is to apply errors and multiple return values. Simply - don’t panic.
- recover
The first statement enables putting the execution of a function on hold. Panic arises during runtime if an unexpected condition occurs during execution. If that happens, the program starts “panicking”. Recover (as name suggests) is a function that recovers from a panicking goroutine. In standard execution, a call to recover will return nil and have no other effect. You have to use it inside deferred functions.
Read the full blogpost about Defer, panic, and recover functions.
What also might interest you is the fact that panic/recover is often used to detect and identify a code smell. What makes the code “smelly”? Everything in the source code of a program possibly signals a deeper problem.
The exception handling processes in both programming languages are superficially similar. If you take a closer look, you’ll see the differences. In the Go language, you freeze the function in some way, and the exception occurs as a panic. Python provides you with more complex solutions with different potential endings, despite the situation.
Go error handling using values
In Go, the usual error handling leverages multi-value returns. If any of returned values complies with the error interface it should be checked for the existence of an error. Consider the following scenario:
if name == "" {
return "", errors.New("name is empty")
}
return "Hello " + name, nil
}
func main(){
var err error
var greeting string
greeting, err = greet("")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
} else {
fmt.Println(greeting)
}
greeting, err = greet("Jimmy")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
} else {
fmt.Println(greeting)
}
}
In this scenario, we have a function greet which takes a name and returns a greeting. In the case of an empty name it fails and returns an error. The first call will result in printing "name is empty" and the second one will print "Hello Jimmy". This is a simple example, but it shows the main idea of multi-value returns with errors. With this pattern, any developer using a function is aware of whether the function can result in an error just by looking at its signature. With the panic/recover mechanism, anyone wanting to use the function would need to inspect the underlying implementation.
Additionally, any error should be handled only once. This means that any time an error happens it should be either logged, passed on, stored, or handled in place. Handling an error this way simplifies the flow and makes code behavior more predictable since ultimately the error is handled in a single place without any side effects occurring somewhere deep in the code.
One of the most popular complaints about Go (especially from newcomers) is the "if err != nil {...}" pattern. Many say that it clouds the code and makes it difficult to read. However, there are patterns (such as one-line ifs) that can simplify the "if err != nil {...}" waves. Here is Rob Pike's (one of Go’s creators) take on error handling, which also addresses this issue - click here .
Dependency management in Go and Python
Dependency is a relationship between two components where the behavior or implementation of one is strongly dependent on the other. In practice, dependency management is every operation aimed at identifying, resolving, and patching dependencies. One example is integrating libraries and packages into applications. How do Go vs Python handle dependency management for the user?
Dependency management in Python
Python provides a few tools for dependency management. Choosing one of them, you should bear in mind that Python is widely used in various applications, and specific tools are better-suited to certain kinds of project; as briefly described below:
- pip
- a system to install and manage software packages. If you’re using the up-to-date version of Python (not older than Python 2.7.9 and Python 3.4) pip is already preinstalled.
- Pipenv
- is a fusion of Pipfile, pip, and virtualenv. It automatically creates a virtualenv for projects, and adds/removes packages when you install/uninstall them.
- Poetry
- allows you to build and track your packages, and share them - if you want.
Dependency management in the Go language
The Go creators proposed modules (modules equals external packages) as a solution for dependency management. The whole process is supported by Go tools like pkg.go.dev to search for needed packages. The Go.mod file
defines each module with its properties and dependencies (both on other modules and the version of Go programming language).
Go offers a unified solution regardless of the version you’re using (so long as it’s newer than 1.11, but we’re sure that you haven’t used that for a long time). On the one hand, it could be taken as an advantage - you haven’t sought for and installed any additional tools. On the other hand, there is no one-size-fits-all solution in programming, and sometimes lack of choices can be limiting.
Does Python or Go support concurrency?
Concurrency is the ability to execute multiple processes, seemingly at the same time. One of the advantages of this approach is saving time, which is not the case when you’re waiting for one task to complete before the next. Looking at Go vs Python support concurrency - it’s worth distinguishing between them.
Python doesn’t natively support concurrency, but provides some solutions to achieve concurrency, like:
- threading - a thread is a set of operations which can be executed independently of others,
- asyncio - a dedicated library to write concurrent code with the help of async/await syntax,
- multiprocessing - Python supports multiprocessing by sending tasks to different processors.
The Go programming language is well-known for its strong support for the concurrency paradigm. Goroutines and channels are the greatest helpers:
- Goroutines - a function which is capable of running concurrently with others.
- channels - are the connectors between Goroutines. They enable communication and synchronization between them.
Both languages offer solutions to manage concurrency. But in this battle, the Go programming language wins - Goroutines and channels support it from the beginning, and the whole language was created with supporting concurrency in mind.
The Go and Python communities
In this case, there are more similarities than differences. Both languages are supported by strong communities - well-development channels on GitHub (Python , Go
), blogs like RealPython
- with tons of useful tutorials - or Go blog
which is supported by the Go creators who themselves write some of the articles. However, there is a large discrepancy between the active developers in Go vs Python communities. Let’s see the statistics
:
- Go, 2.1 M
- Python, 10.1 M
Python community is much bigger but it has been growing over the years while Go is pretty new in the game.
Active and large communities translate to complex, curated and regularly updated libraries and frameworks for both the Go language and Python. It doesn’t matter whether you choose the Go language or Python, you can count on the community's support and a variety of sources for tips, tricks, and tutorials.
It is also good to know about the weaknesses of the solutions you’re considering, to be aware of what could be a barrier during project development.
Disadvantages of Python and Go
We all know there is no one solution that performs for everyone in every project. That’s why it is better to know the drawbacks beforehand and make a wise decision. While using Go, you should be ready for a lack of generics, and a simplicity that can sometimes be a limitation instead of a benefit. The biggest disadvantage of Python is its slow speed. You should be aware that this is not the best choice for mobile development, it’s not suitable for low-level programming, and is seen as limited for database access.
These are the general disadvantages of both programming languages. They are mentioned only superficially here and you might wonder why. The answer is really simple - the disadvantages are subjective and don't have to be a barrier or weakness for every project. So there is no reason to focus on them unduly. It is more helpful to focus on looking at which types of projects best suit each language.
In which projects might Python perform better?
Of course, there is no one strict list of projects for which Python always works. However, in some cases its features can perform better than other languages. You can consider Python if your project involves:
- AI and machine learning
- Web development
- Programming application
At CodiLime, we benefited from Python during a project for our Internet Service Provider client. In this case study we describe how we built a web application for network monitoring in heterogeneous environments.
Could the Go programming language be chosen for similar projects to Python? Knowing the differences between them, you might guess that the answer is probably no. And you’d be right. Below are a few examples when Go can meet project expectations better.
In which projects might Go perform better?
Are you still hesitating to use Go in a project? We prepared an in-depth article on why Golang may be a good choice for your project, including Go use cases, and the benefits both for programmers and business, gathered for you.
Generally, Golang’s strengths are that it is lightweight and quick to compile, which can be useful in fields like:
- Cloud services
- Microservices
- Media platforms
In this article you can find more information about companies using Go. There are some big names, like Uber or PayPal - so the variety of industries is quite impressive.
Do you want to develop or build a project in Golang? Check out:Golang development services
Conclusion
To sum up, both Go and Python have their pros and cons - each one could perform better in different types of projects. It is good to know how Go vs Python perform - that is the reason why the idea of this simple guide to the main differences between these programming languages first arose. Hopefully, this will help you use Go or Python wisely in your next project - or to find a developer who knows your chosen language inside out and will take your project to the next level.










